Latinos See the Highest Increases and Levels of Working Poverty in Many Regions
As Latinos drive population growth and change in America, their ability to thrive is increasingly critical to the health of our economies locally and nationally. Yet, new data on working poverty in the National Equity Atlas reveals the extent to which many Latinos are working full-time yet still struggling economically. In 2012, nearly one in three Latino full-time workers, ages 25 to 64, earned below 200 percent of poverty – up from 27 percent in 1990 and compared with 9 percent for their White counterparts.
This post takes a closer look at Latino working poverty across the nation’s largest 150 metropolitan regions. Working poverty describes full-time workers with a family income below 200 percent of poverty, and the rates of working poverty in this post reflect the working poor as a share of full-time workers ages 25 through 64. While poverty is defined at the family level, based on combined income from all family members, in this post we make reference to individual earnings for simplicity. Given that an individual’s family income must be as high or higher than their personal earnings, the rates of working poverty reported here understate the rates that would be found if only an individual’s earnings were considered.
Latino Working Poverty High and Increasing in Many Regions
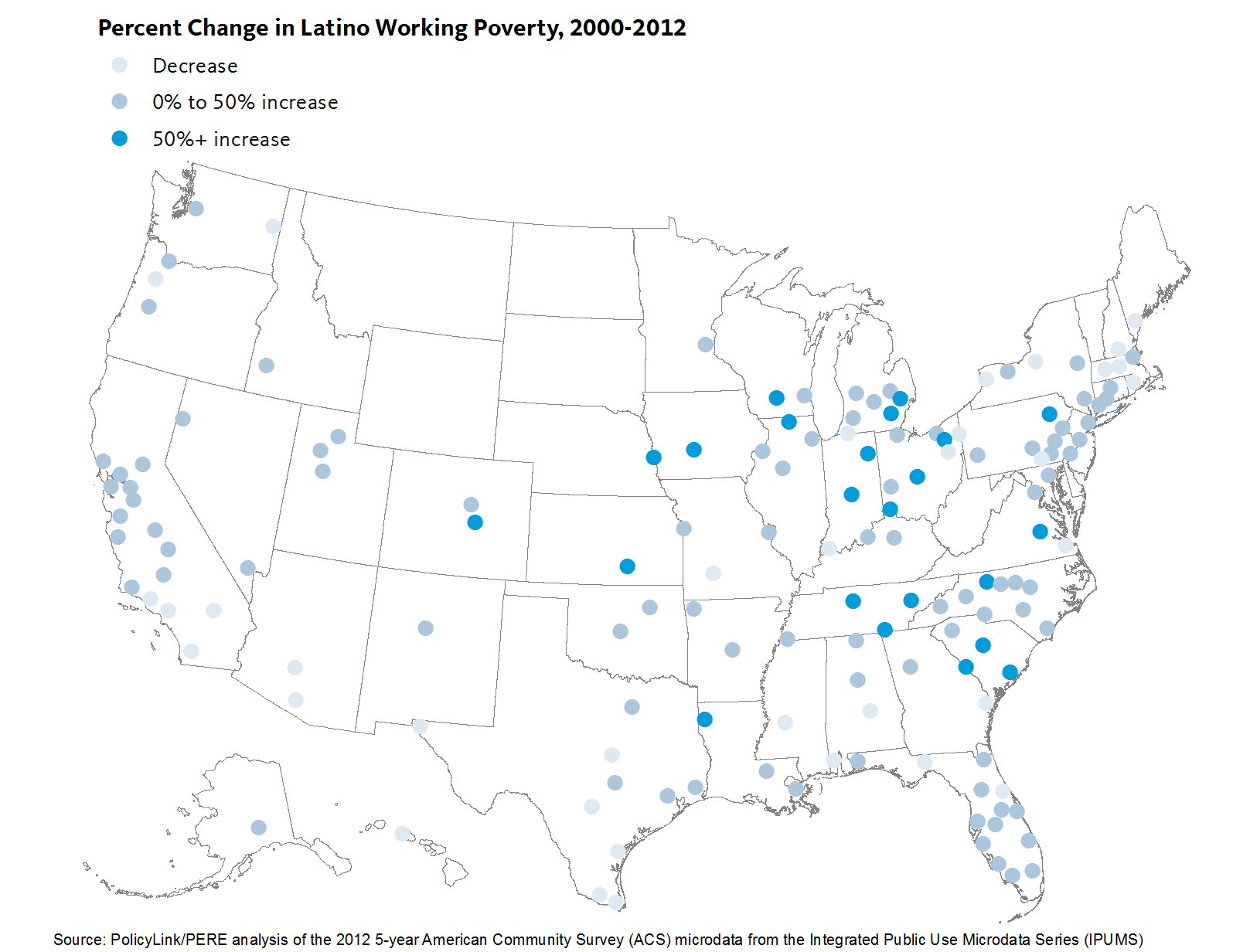
Not only do many regions have high rates of Latino working poor, conditions are getting worse over time. This is shown by the scatter plot below, which plots the largest 150 regions by the share of Latino full-time workers who earn below 200 percent of poverty in 2012 and the percent increase in Latino working poverty between 2000 and 2012. The farther to the right, the greater the share of Latino working poverty in 2012. The higher up on the chart, the greater the percent increase in Latino working poverty between 2000 and 2012. As illustrated by the number of metros in the upper-right quadrant, there appears to be a positive relationship: the regions with higher rates of working poverty among Latinos also saw a sharp growth in Latino working poverty.
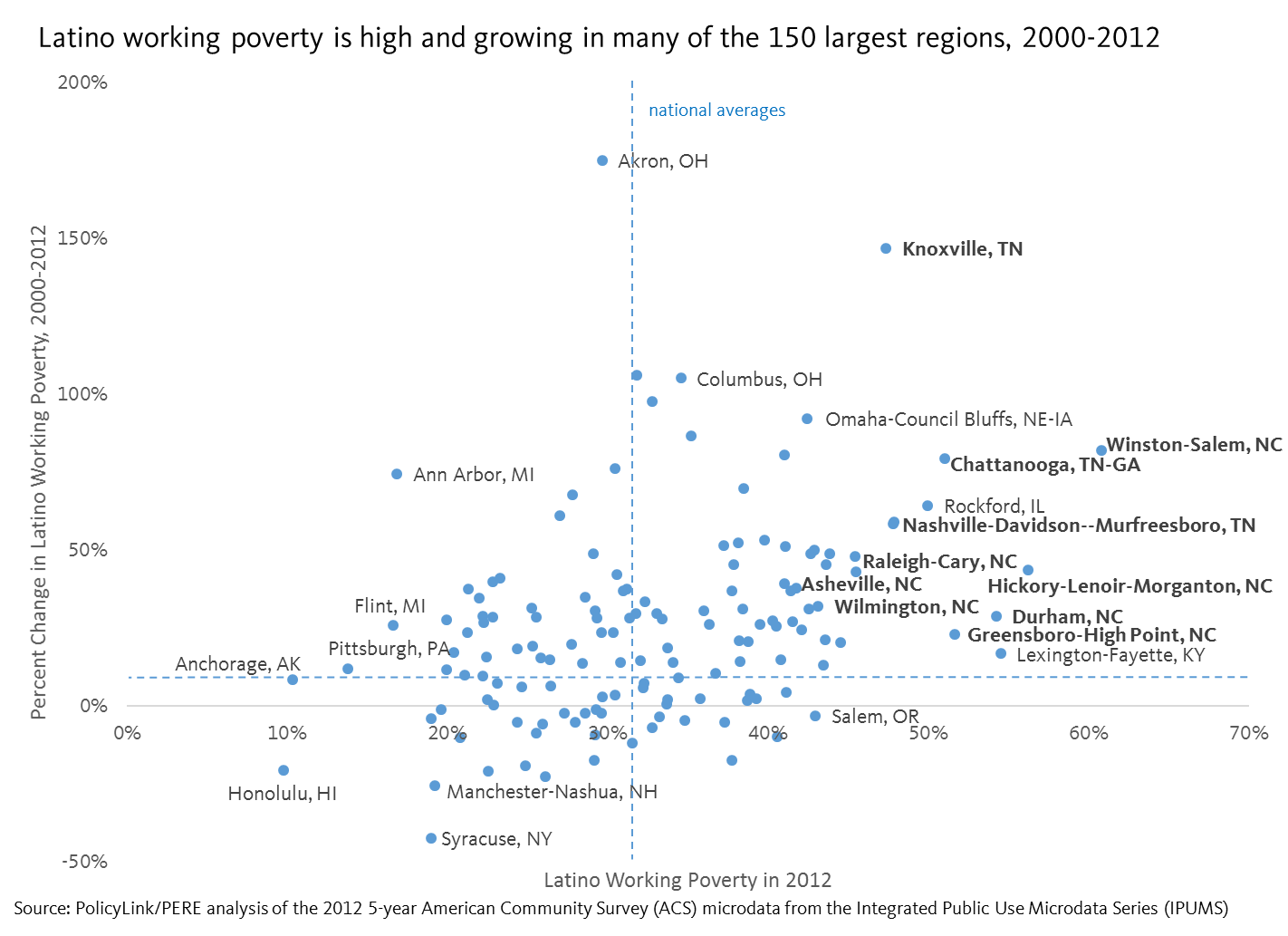 Regions in Tennessee and North Carolina have the highest rates of Latino working poverty
Regions in Tennessee and North Carolina have the highest rates of Latino working poverty
Mapping the data reveals additional geographic patterns, including the clustering of Latino working poverty in the South and particularly in the states of Tennessee and North Carolina. Of the largest 150 metro regions in the U.S., all nine in North Carolina saw substantial increases in working poverty among Latino full-time workers, ranging from a 23 percent increase in Greensboro to an 82 percent increase in Winston-Salem. Each region also had a Latino working poverty rate greater than the national average except for Fayetteville, which matched it. More than half of Latino full-time workers in Greensboro, Durham, Hickory, and Winston-Salem earned less than 200 percent of poverty.
Similarly, the four regions in Tennessee included in the Atlas saw higher than average increases in the overall rates of Latino working poverty. One in two Latino full-time workers in Chattanooga earned less than 200 percent of poverty in 2012, up from 28 percent in 2000. Over the same time period, the Latino population grew significantly faster than any other group in the region.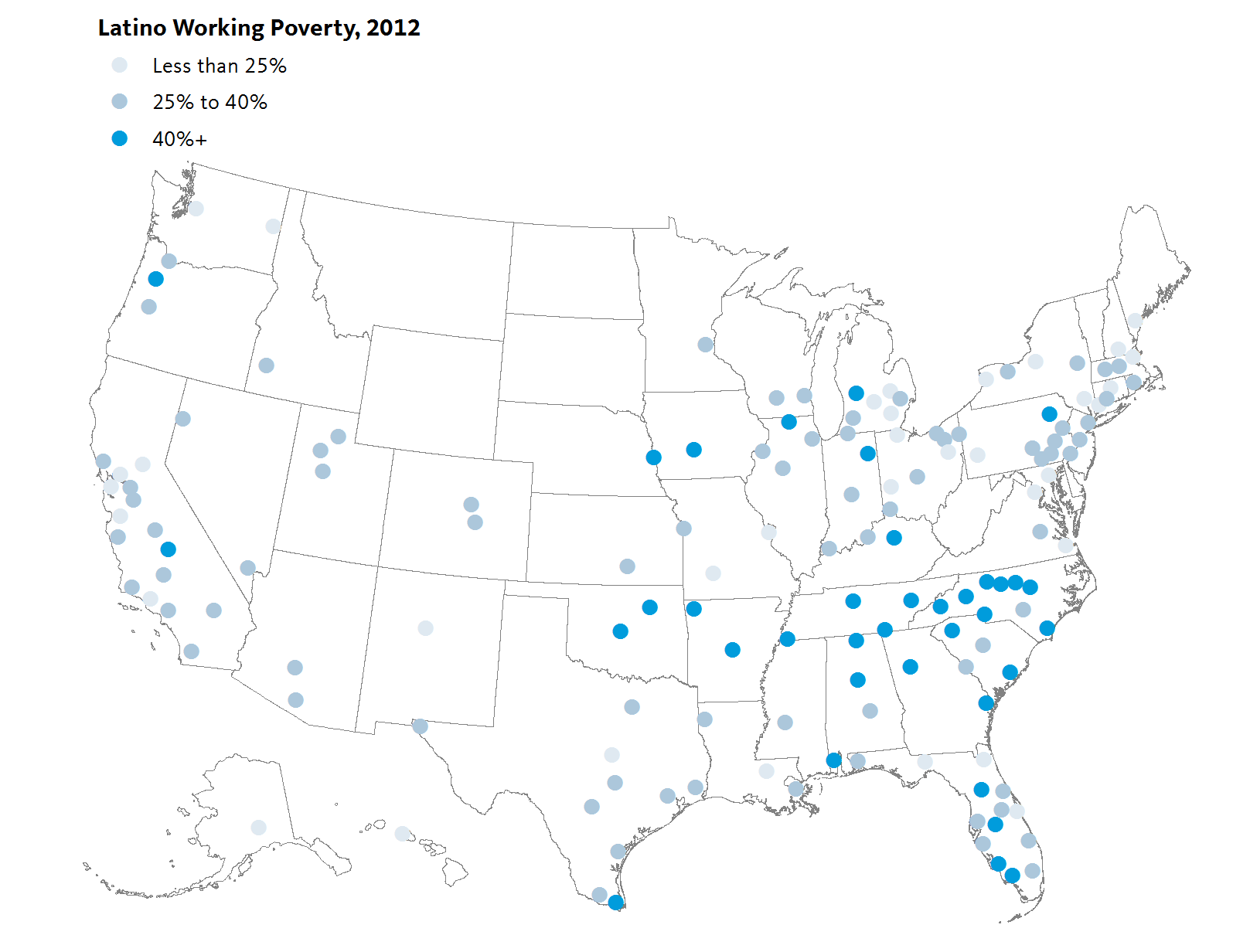
Tennessee and North Carolina are among the roughly 15 states that currently ban local governments from adopting their own minimum wage laws. Part of the controversial HB2 law passed earlier this year in North Carolina, which restricts usage of multiple occupancy bathrooms for transgender and gender non-conforming people, also includes state preemptions to local minimum wage increases. The current minimum wage in Tennessee and North Carolina is the same as the federal: $7.25 an hour. The MIT Living Wage Calculator, however, estimates that a living wage for a family of four ranges from $13 to $22 an hour in Tennessee and from $14 to $23 an hour in North Carolina. The state preemption laws also prevent localities from allowing workers to earn paid sick leave.
This is a growing and alarming trend: eight states have considered restrictions on local minimum wage increases this year and the story is often similar. When states fail to pass increases in minimum wages in step with increases in cost of living and inflation, some jurisdictions take matters into their own hands by increasing local minimum wages. State legislatures—especially those led by Republicans—push back by adopting laws preventing local action. Raising wages would be especially beneficial to workers of color. In North Carolina, for example, 11 percent of White full-time workers earn less than 200 percent of poverty compared with nearly half of Latino full-time workers. Even more striking, 12 percent of Latino full-time workers earn less than 100 percent of poverty.
Addressing working poverty is a moral and economic imperative. If Latinos, the fastest growing group in many regions, are unable to participate, prosper, and reach their full potential, the impacts will go far beyond the Latino population. To learn more about working poverty in your city, region, or state, and learn about policies that lift the wages of workers, explore the new working poor indicator.